- January 30, 2025
Stress vs. Anxiety: How to Tell the Difference
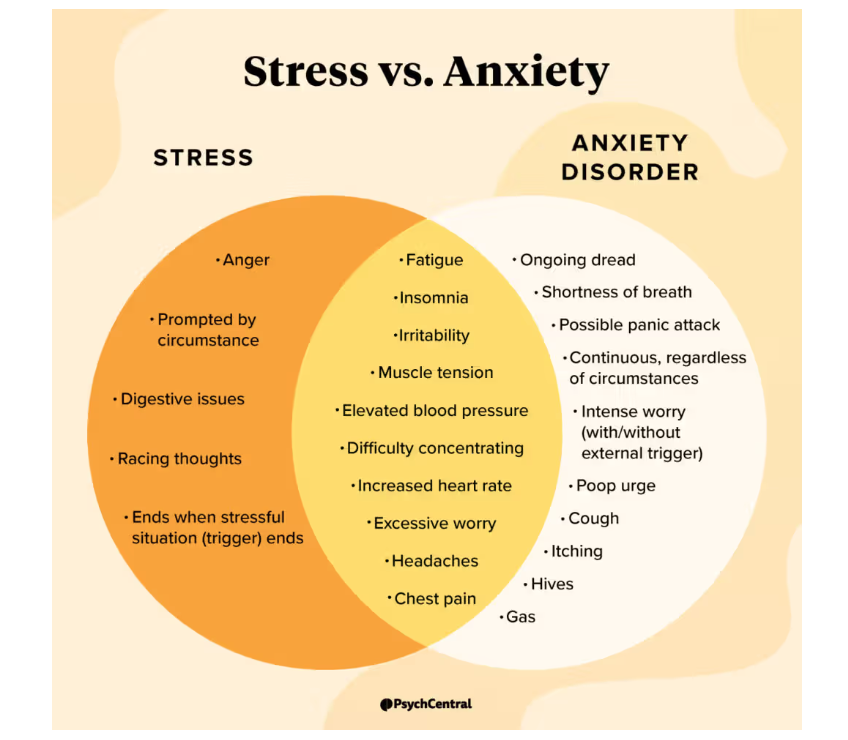
Stress and anxiety are often used interchangeably, but they are distinct experiences. Both are natural responses rooted in the body’s fight-or-flight mechanism, which helps us react to threats. However, stress is usually short-term and linked to a specific situation, while anxiety often lingers and may occur without a clear cause.
Understanding these differences is essential for managing both effectively.
Stress typically arises from identifiable challenges, such as a work deadline, an exam, or a major life event. It triggers the release of stress hormones, which increase heart rate, heighten senses, and provide energy to respond to a threat. Once the situation resolves, the body returns to its normal state.
Anxiety, on the other hand, can feel less predictable. It may persist even after the initial stressor is gone or appear without an obvious trigger. Anxiety manifests as persistent worry, unease, or dread. While these feelings can motivate action or prepare someone for potential danger, excessive anxiety can interfere with daily life.
Both stress and anxiety share physical symptoms, such as muscle tension, irritability, and trouble sleeping. This overlap can make it difficult to distinguish between the two. The key difference lies in their duration and triggers: stress is a reaction to a specific situation, while anxiety may be ongoing and harder to pin down.
Managing Stress and Anxiety
Stress and anxiety can be managed through simple yet effective strategies. Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga, can calm the mind and body. Physical activity, like walking or running, helps release tension and improve mood. Talking with someone you trust can also provide relief and perspective.
However, if stress and anxiety become overwhelming or start to disrupt everyday life, professional help may be necessary. Chronic stress or anxiety disorders can lead to more severe issues if left untreated.
When to Seek Help
It’s important to recognize when stress or anxiety requires medical attention. Warning signs include:
- Persistent worry or fear that interferes with daily activities
- Relying on alcohol or drugs to cope
- Difficulty sleeping or significant changes in eating habits
- Feelings of hopelessness, self-harm, or suicidal thoughts
If you notice these signs, reaching out to a doctor or mental health professional is essential. Early intervention can help prevent further emotional and physical strain.
The Bottom Line
Stress and anxiety are normal reactions to life’s challenges, but they serve different roles. Stress is the body’s response to a clear threat, while anxiety is its reaction to stress or an ongoing sense of unease. Both can be managed with relaxation, exercise, and support from others.
When stress or anxiety becomes a persistent problem, seeking help can lead to relief and better mental well-being.

